Discover the HACCP Steps Defined by the Codex Alimentarius
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a systematic, preventive approach to food safety that involves identifying, evaluating, and minimizing or controlling hazards. The goal of an HACCP plan is to prevent, eliminate, or reduce hazards to an acceptable level by focusing on three key factors:
- Securing a strong commitment from the management team
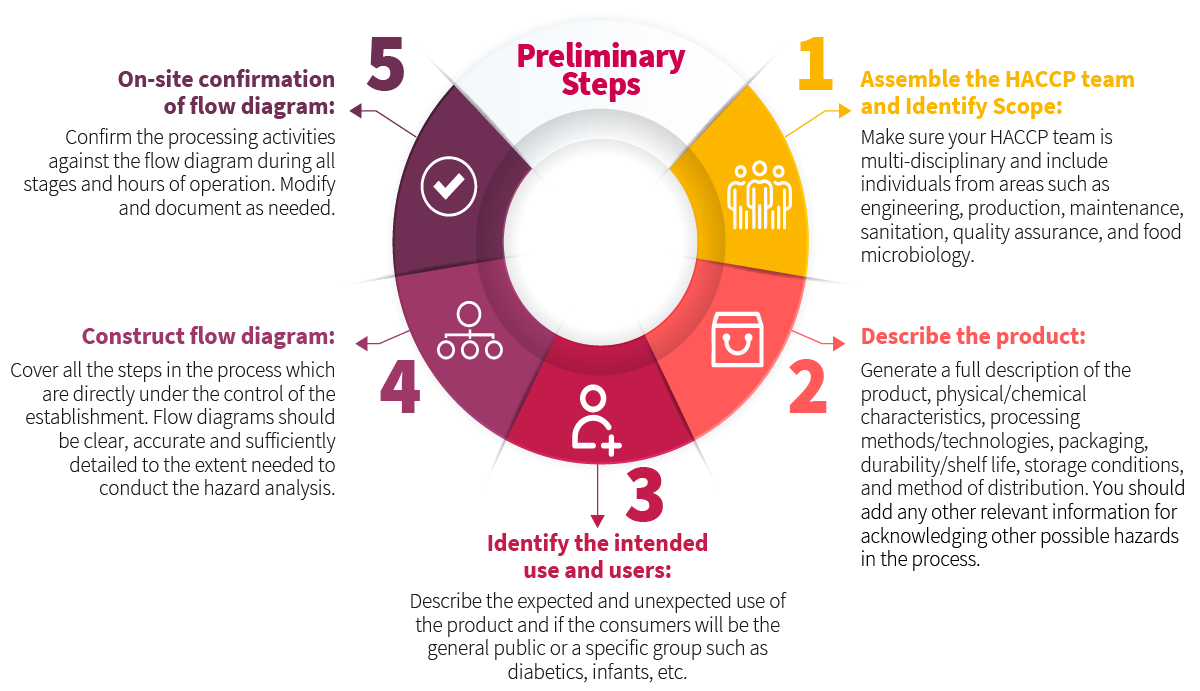
- Ensuring all members of the HACCP team are familiar with the methodology, which includes five preliminary steps and seven principles
- Training all personnel to implement the HACCP steps
Having worked in the food industry for many years does not automatically qualify you as an HACCP expert or even as a trained member of the team. An HACCP team is assembled to address food safety by evaluating, minimizing, and controlling biological, chemical, and physical hazards throughout raw material production, procurement, handling, manufacturing, and distribution. This means you must know the HACCP principles and be HACCP trained to join this team.
With more access to powerful communication tools, like the Internet and social media, consumers have become more informed and selective when choosing products. Negative publicity about recalls will get widely distributed around the world, so having a strong HACCP program in place can help protect your business, reputation, and the integrity of your food products.
HACCP steps and principles have been successfully applied in many food and beverage manufacturing, packaging, and processing plants, as well as food storage warehouses. The seven principles of HACCP have been accepted by many government agencies, trade associations, and the food industry at large.
Understanding the Codex Alimentarius
The Codex Alimentarius is a collection of internationally recognized standards, codes of practice, guidelines, and other recommendations published by the Codex Alimentarius Commission, to ensure consumer health and fair practices in the food trade.
The Codex Alimentarius covers all foods, whether processed, semi-processed, or raw. It contains general standards covering food labeling, food hygiene, food additives, and pesticide residues. The standards also include procedures for assessing the safety of foods derived from modern biotechnology, as well as good hygiene practices (GHP) and the HACCP guidelines.
According to the AIB International Consolidated Standards for Inspection, for products that aren’t required to have a regulated food safety plan, a program with HACCP steps and principles based on Codex Alimentarius must be written and implemented.
HACCP Around the World
Although HACCP steps and principles were developed for international use, its implementation varies by country, with subtle differences in the foods covered and the specific requirements enforced.
- The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has mandated that manufacturers of meat and poultry have a written HACCP plan.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which operates in the U.S., has mandated that the seafood and juice products have a written and implemented HACCP plan.
- Food businesses in Europe are legally responsible for the safety of the food they produce, transport, store, and sell. Across the European Union, these business operators are required to put in place, implement, and maintain a permanent written procedure(s) based on HACCP steps and principles.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has been building capacity in the implementation of HACCP in numerous countries, including Albania, Croatia, Cyprus, Greece, Montenegro, Republic of Moldova, and Romania.
- For most food businesses in Australia, having a food safety program based on the principles of HACCP is a legal requirement. Standards 3.2.1 of the Food Standards Code outlines this requirement.
- The Quality Council of India has launched two certification programs, “IndiaGHP” and “IndiaHACCP,” based on the globally accepted Codex Standards. These schemes aim to help food manufacturers and supply chain operators demonstrate compliance with global standards without having to obtain foreign certifications related to HACCP or Good Hygiene Practices (GHP).
- Having an HACCP certification is not mandatory in Nigeria, but the Nigerian Export Promotion Council (NEPC) is urging local food producers and exporters to participate in an HACCP certification process so their export opportunities can improve as they meet the criteria established by the European Union and other countries.
- Mexico has the legislation NOM-251-SSA1-2009, which defines minimum requirements for good hygiene practices during the manufacturing process of food, beverages, food supplements, and their raw materials. Even though the legislation addresses HACCP, it establishes that “each company must take responsibility for the application of the principles of the HACCP system; however, the government and companies are aware that there may be obstacles to the effective implementation of such a system by the company itself.”
Qualifying to Join an HACCP Team
Joining an HACCP team is a serious responsibility, but the process to become eligible will ensure you’re prepared to meet its demands. You can become a member of your facility’s HACCP team by successfully completing AIB International’s HACCP Online course or enrolling in one of our upcoming virtual workshops.